Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Name
- Supplied By
- Cleaning Ingredients Functions
- Industrial Additives Functions
- Technologies
- Product Families
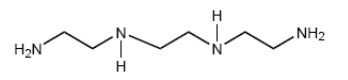
- Chemical Structure
Features & Benefits
- Labeling Claims
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Segments
- Applications
- Applicable Processes
- Industrial Additives End Use
Properties
Regulatory & Compliance
- Chemical Inventories
Safety & Health
- Safety Information
- Because of the fragility of eye tissue, almost any eye contact with any ethyleneamine may cause irreparable damage, even blindness.
- A single, short exposure to ethyleneamines, may cause severe skin burns, while a single, prolonged exposure may result in the material being absorbed through the skin in harmful amounts.
- Exposures have caused allergic skin reactions in some individuals.
- Single dose oral toxicity of ethyleneamines is low.
- The oral LD50 for rats is in the range of 1000 to 4500 mg/kg for the ethyleneamines.
- The principal hazards that arise in working with triethylenetetramine (TETA) are those associated with similar organic amines; namely, a corrosive action on skin and eyes.
- Precautions should be taken to prevent contact with these parts of the body such as by use of protective clothing and chemical goggles.
- If contact occurs, immediately flush the exposed area with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes.
- Eye exposures should be examined by a physician. Contaminated clothing should be laundered before reuse.
- If ingestion occurs, do not induce vomiting.
- Have the individual drink a large amount of water (or milk, if it is readily available) and transport them to a medical facility immediately.
Packaging & Availability
Storage & Handling
- Storage Conditions
In order to maintain the high degree of purity with which triethylenetetramine (TETA) is manufactured and shipped, the following storage and handling considerations are recommended
Dry Inert Gas Blanket
TRIETHYLENETETRAMINE (TETA) should be stored under a dry inert gas blanket, such as nitrogen, to minimize contamination resulting from contact with air and water.
Materials of Construction
- If slight coloration of the ethyleneamine is acceptable, storage tanks may be made of carbon steel or black iron, provided they are free of rust and mill scale.
- However, if the amine is stored in such tanks, color may develop due to iron contamination.
- If iron contamination cannot be tolerated, tanks constructed of types 304 or 316 stainless steel should be used.
- (Note: Because they are quickly corroded by amines, do not use copper, copper alloys, brass, or bronze in tanks or lines.)
- Recommended storage construction for TETA is stainless steel.
Storage Temperature
- Triethylenetetramine (TETA) has a pour point of -35.1°C.
- To avoid freezing, the product should be maintained above this temperature.
Spills or Leaks
- Small spills should be covered with inorganic absorbents and disposed of properly.
- Organic absorbents have been known to ignite when contaminated with amines in closed containers.
- Certain cellulosic materials used for spill cleanup such as wood chips or sawdust have shown reactivity with ethyleneamines and should be avoided.
- Large spills should be contained and recovered.
- Water may be used for clean-up purposes, but avoid disposing of the material into sewers or natural water bodies.
- Disposal should be in accordance with all federal, state and local laws, regulations, and ordinances.
- Ethyleneamine leaks will frequently be identified by the odor (ammoniacal) or by the formation of a white, solid, waxy substance (amine carbamates).
- Inorganic absorbents or water may be used to clean up the amine waste.
